A New Breakthrough in AI Screening for Scoliosis, The Research Results Published in the Sub-Journal of Nature
Scoliosis is the third most prevalent morbidity among adolescents in China and is a major concern for the health of adolescents in the country. About 2-4% of adolescents worldwide have scoliosis. Due to the lack of simple and efficient scoliosis screening technology, most adolescents miss the best period of conservative correction and need surgical treatment, resulting in a heavy family and medical burden.
Professor Yang Jun Lin of the Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao-Tong University found that, to a certain extent, exposing humans back can reflect the degree of scoliosis. In conjunction with Professor Lin Hao Tian, from the Sun Yat-Sen Eye Center of Sun Yat-Sen University, and Professor Liu Xi Yang, from Xidan University; they started to develop deep learning of screening technology for scoliosis. This project received the National Research and Development (R&D) in 2018. The project number is 2018YFC0116500.
The team is the first to develop artificial intelligence (AI) system in globe, which can screen scoliosis based on the appearance of the naked back of a patient's body. The accuracy of this AI screening is similar to a scoliosis expert's knowledge. It is expected to be used in a large scale scoliosis screening. It also provides the possibility to track the trajectory of scoliosis in a crowd.
The research is the world's first large-scale AI screening for scoliosis. To share their results, the professors have published their research on the sub-journal of Nature on October 25th, 2019 with the title "Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for scoliosis screening using back-images." (Communication Biology)

The first time in which large-scale AI scoliosis screening is conducted based on a photo of a person's naked back.
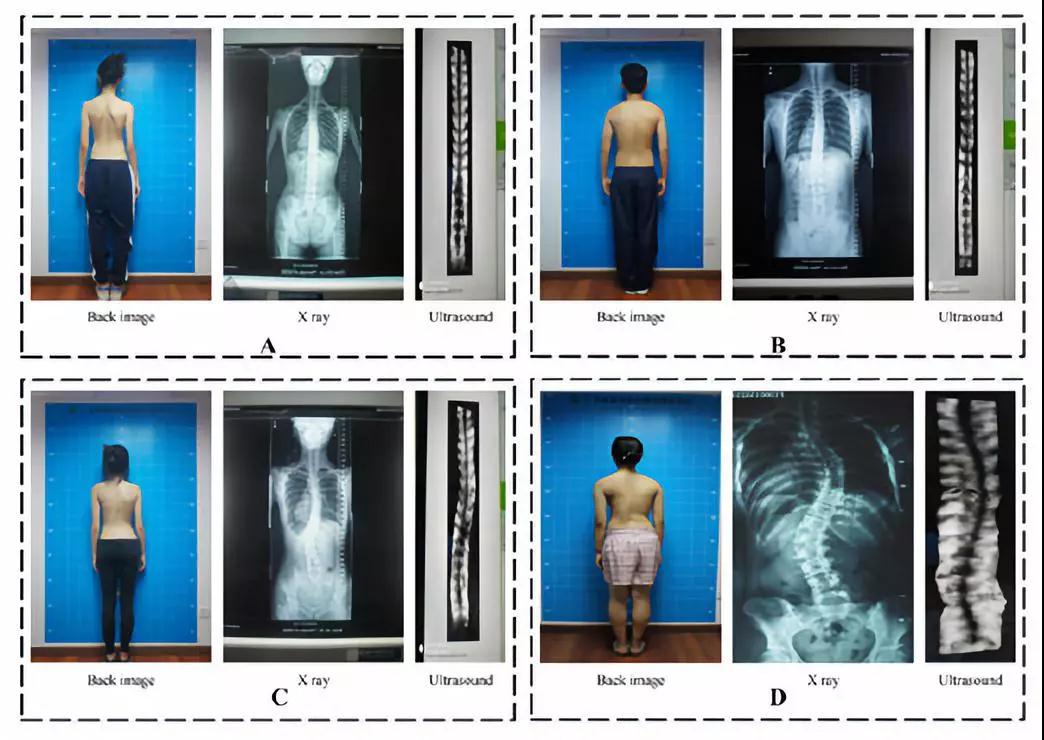
The abnormal development of the spine can change the overall appearance of the back. Such characteristics include high or low shoulders, unequal heights of shoulder blades, and asymmetry of side profiles. Scoliosis experts can diagnose a patient's scoliosis based on the AI screening system. By using a photo of a patient's bareback, experts can identify the problems efficiently and conveniently. Moreover, this AI system lowers the patient's exposure to radiation.
For example, the collaborating team in this study used the patient's x-ray and ultrasound images as a controlled variable to demonstrate the AI's accuracy. By comparing appearance images with the controlled variable, the relationship between the characteristic of the back and the severity of scoliosis is evident. This is a clear example that demonstrates the effectiveness of the AI screening system for testing scoliosis.
Medical artificial intelligence algorithm framework with innovative application that targets monitoring network and evaluation network to score.
The study innovates the target detection network to locate the patient's bareback. Furthermore, multiple convolutional neural networks are used to meet the needs of different screening tasks. The neural network model is used to screen whether adolescents have scoliosis (if the degree of spine curvature is greater than 10), determine whether the patient needs treatment (the degree of spine curvature is greater than 20 degrees), and clarify the range of adolescent spine curvature (0-9 degrees, 10-19 degrees, 20-44 degrees or greater than 44 degrees) with outstanding performance.

The development of an artificial intelligence (AI) scoliosis screening system is expected to overtake traditionally manual screen tests.
In this study, the professors provide the establishment of a high-accuracy and large-scale scoliosis screening system. The results of the study showed that screening and evaluation of scoliosis has satisfactory performance on detecting whether a patient has scoliosis and whether a patient's spine curvature is greater than 20˚.
While validating this system, the accuracy of this AI system has reached a level of average human experts. The speed of screening was faster than manual screening. Therefore, it is possible to conduct large scale scoliosis screening tests. The AI screening system has shown its efficiency. Professors have also pointed out how this screening test can help reduce manpower, resources, and personal training (which was required for manual screening). On top of those advantages, AI screening can be used to monitor a patient's mild progress and reduce a patient's exposure in x-ray follow-up checks.



